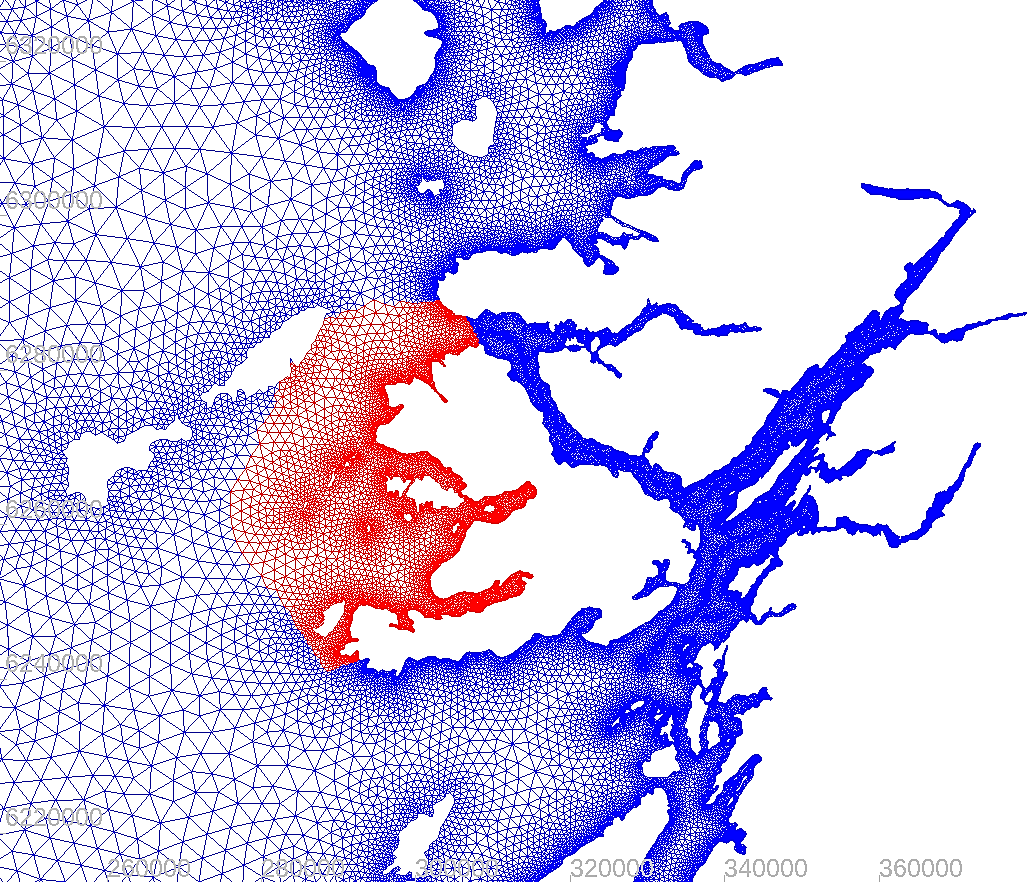
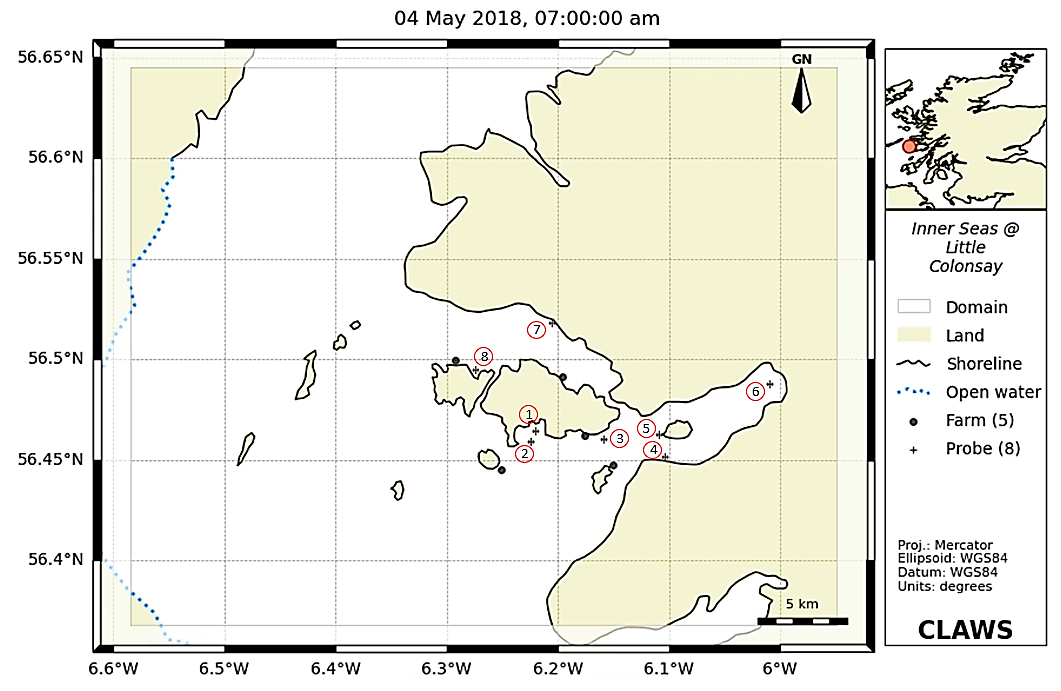
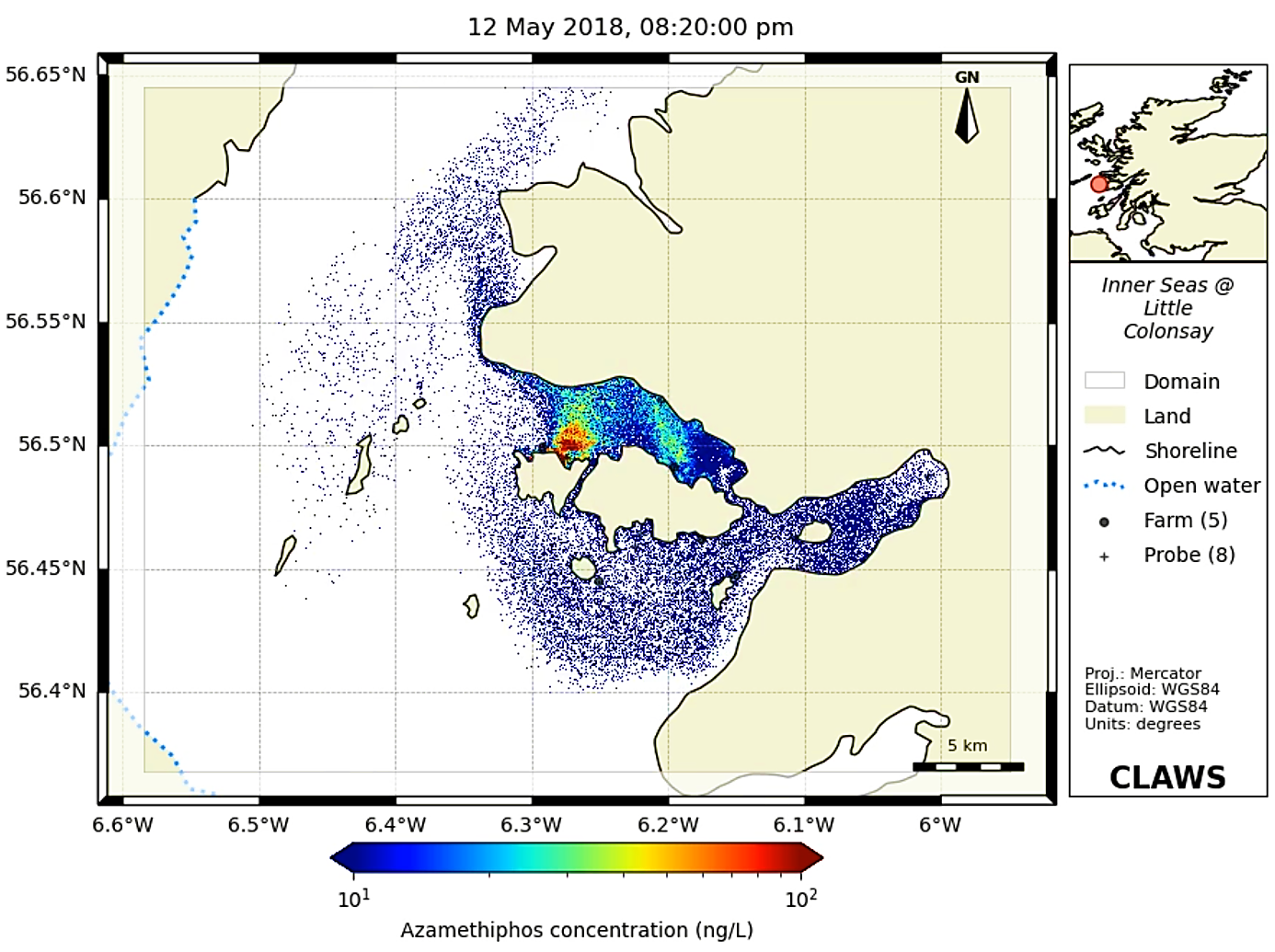
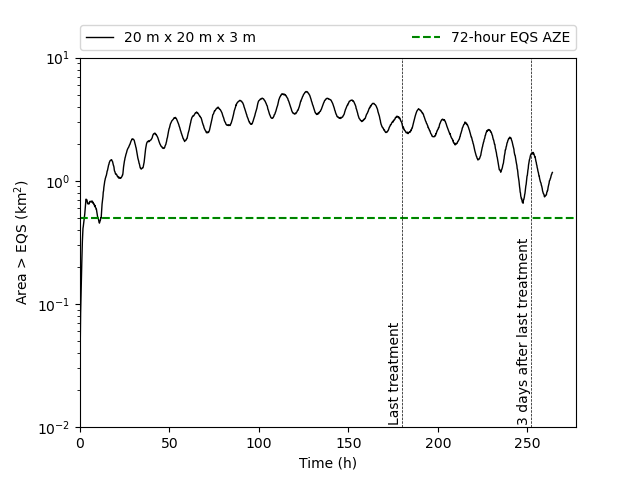
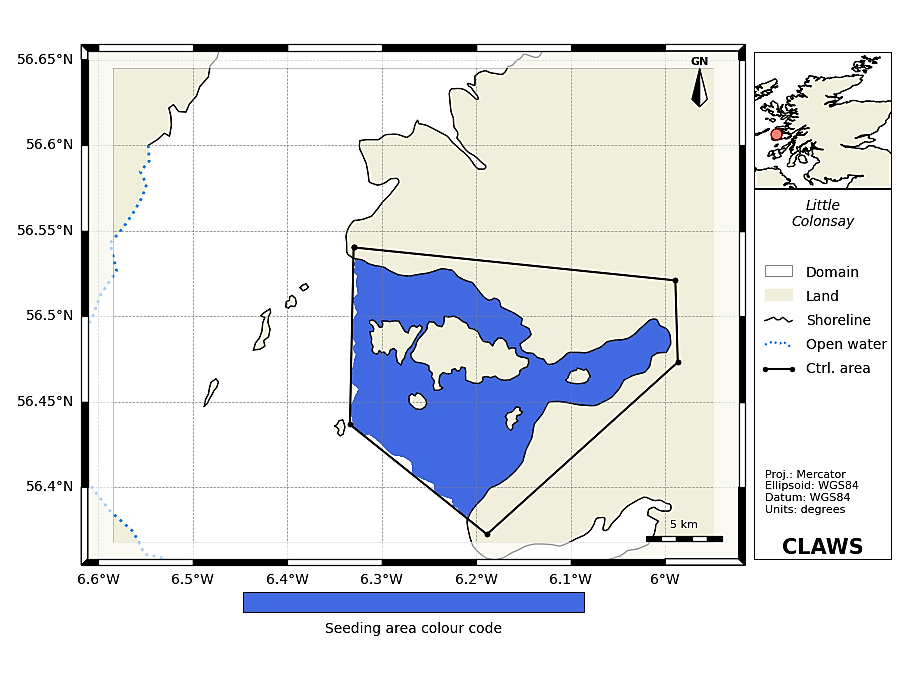
CLAWS – Chemicals for Lice and Waste from Salmon Farms - is a repository of
particle-based models for application in salmon farms in semi-enclosed sea lochs and open sea areas. CLAWS is written in Python and consists of seven modules:
1) Hydrodynamics.
2) Bath treatments.
3) Nutrients.
4) Waste.
5) E. coli.
6) Oyster larvae.
7) Plastic litter.
A more detailed description of each module, together with example applications, is provided in the Documentation section but may be summarised as follows:
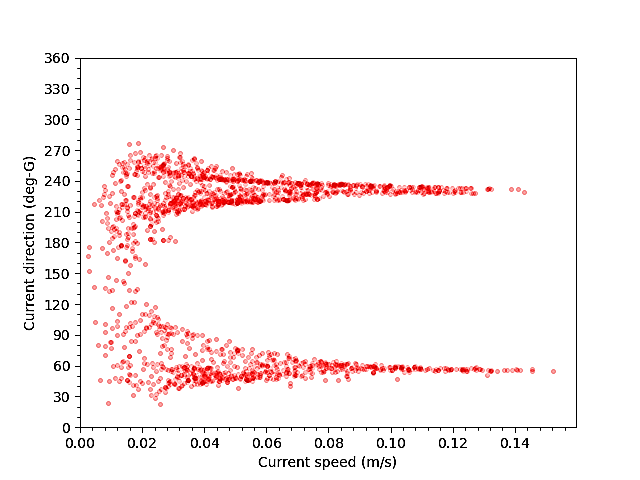
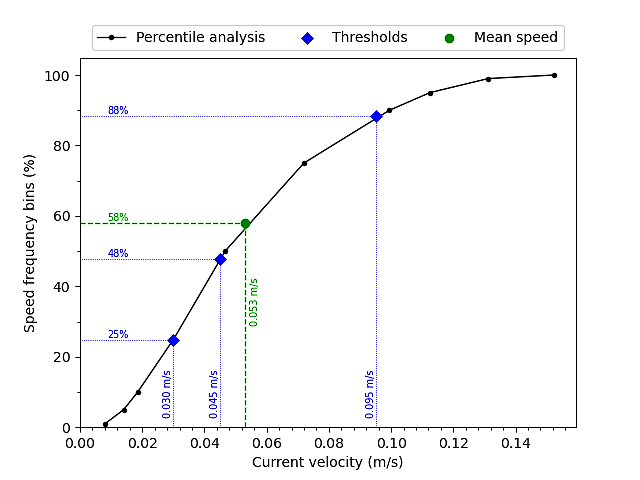
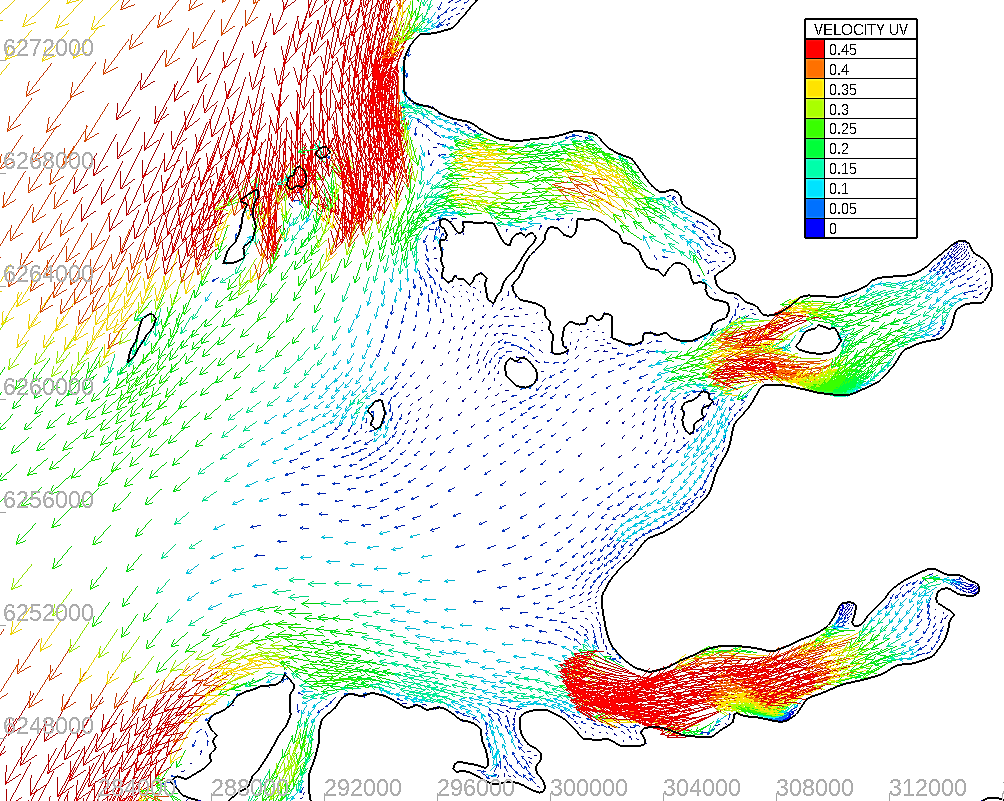
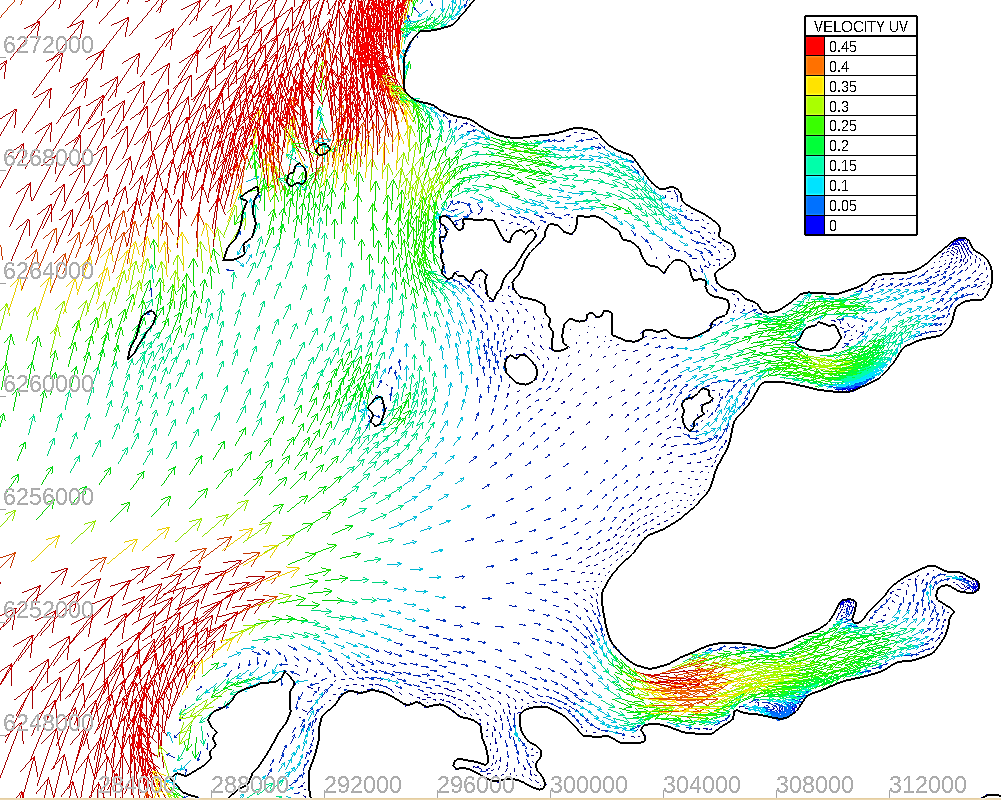
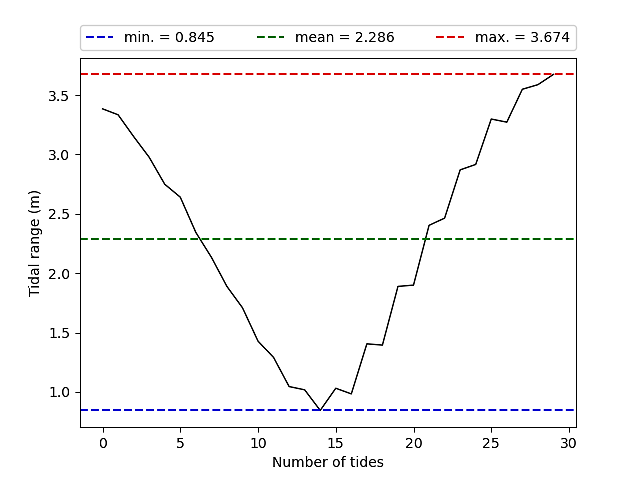
1. Hydrodynamics - Python scripts have been written to allow the user to compare directly modelled and observed data. These data are output in a suitable format to assess how the model data compares against the calibration/validation requirements for hydrodynamic and discharge modelling e.g. the SEPA requirements.
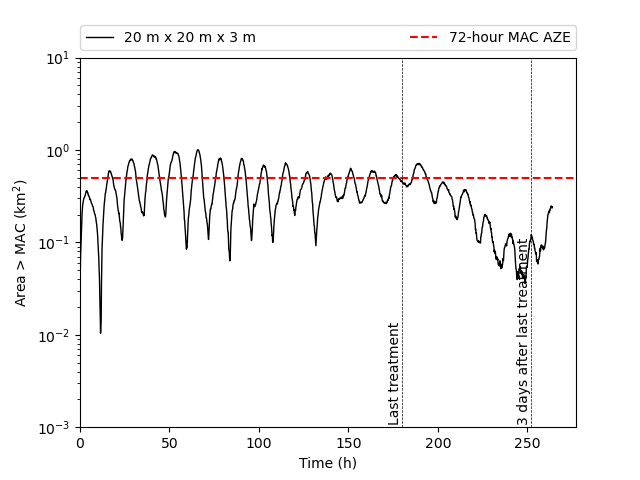
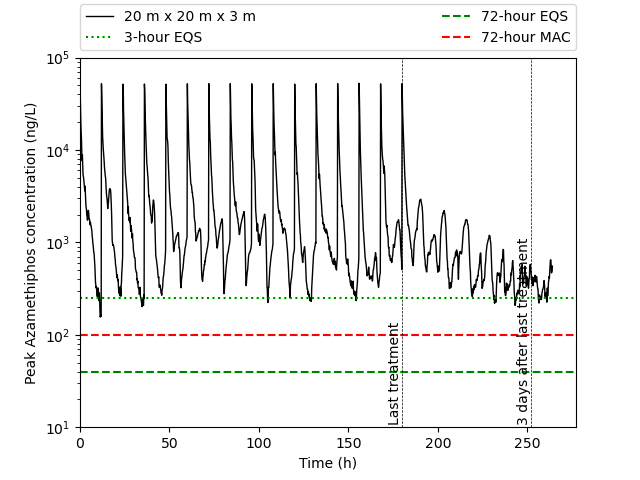
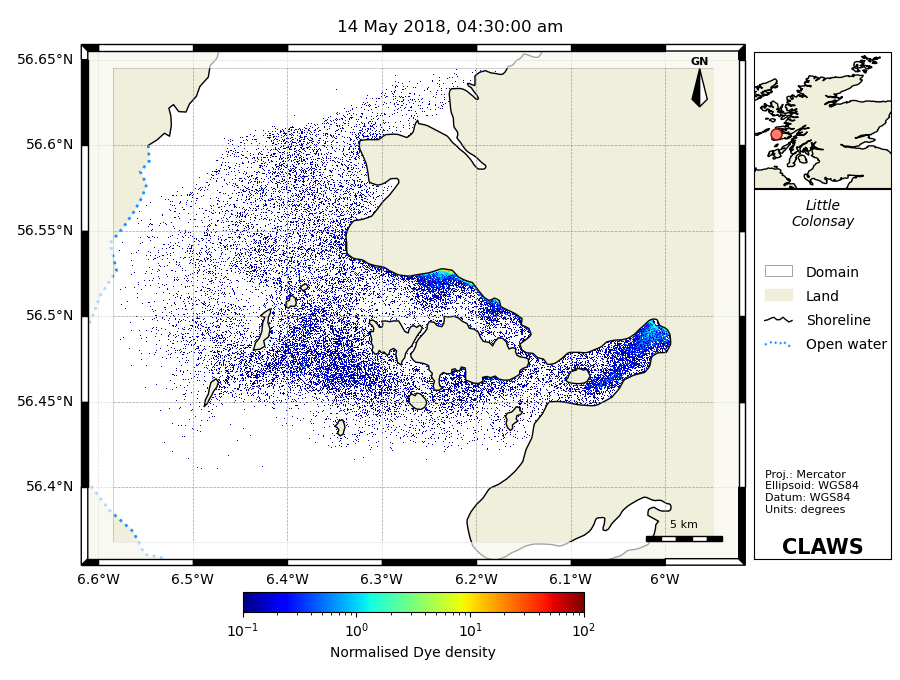
2. Bath treatments - The bath treatment model predicts pesticide dispersion in the marine environment and comparison is made against statutory standards e.g. the SEPA standards for Maximum Allowable Concentration (MAC) and Environmental Quality Standard (EQS). The module can also be used for effluent dispersion.
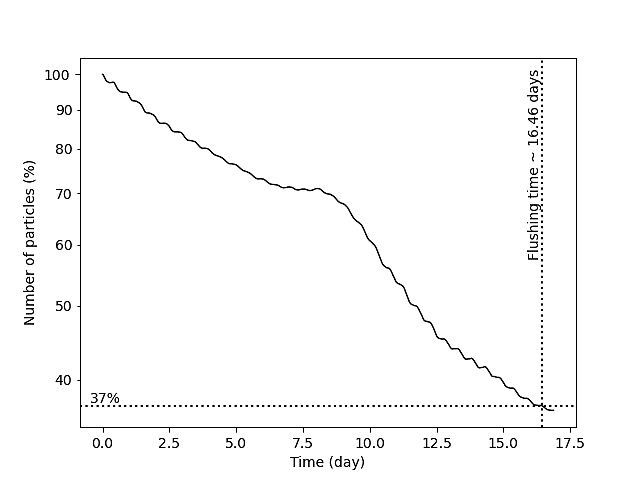
3. Nutrients - This module calculates the sea area, mean height, volume and flushing time prior to deriving an equilibrium concentration enhancement (ECE) index for soluble nitrogen.
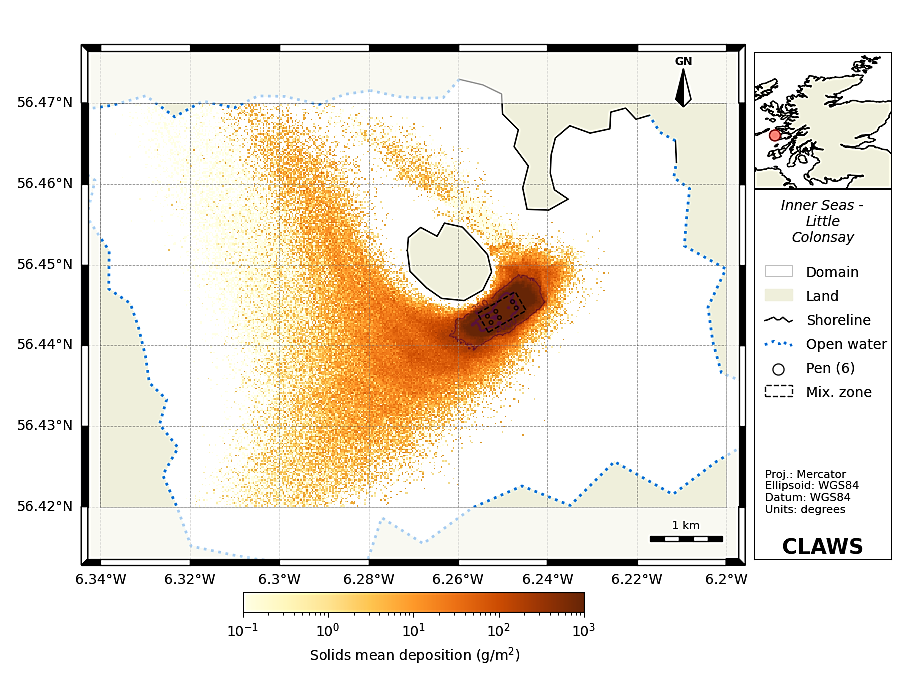
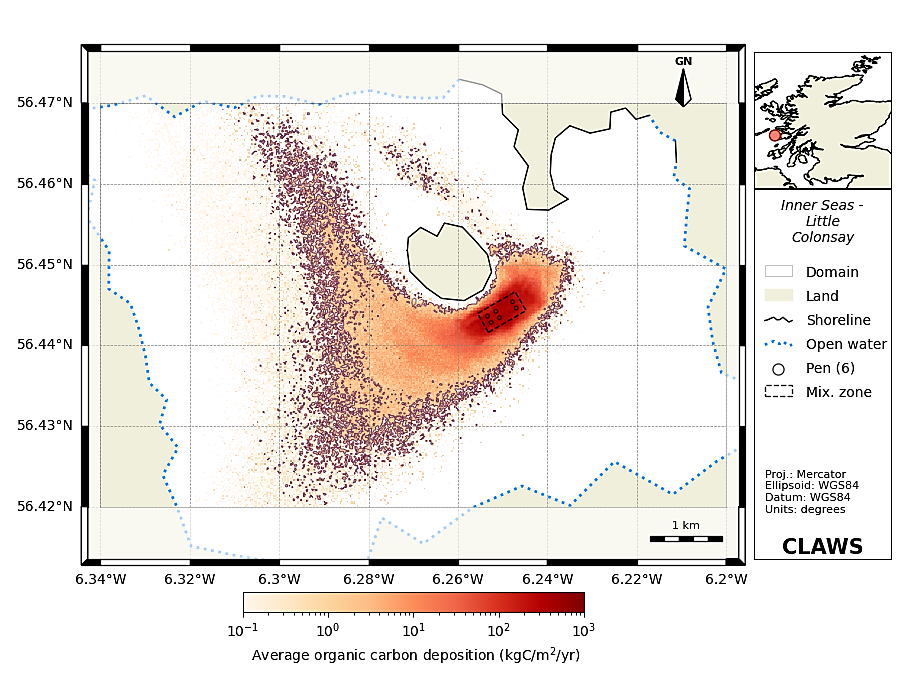
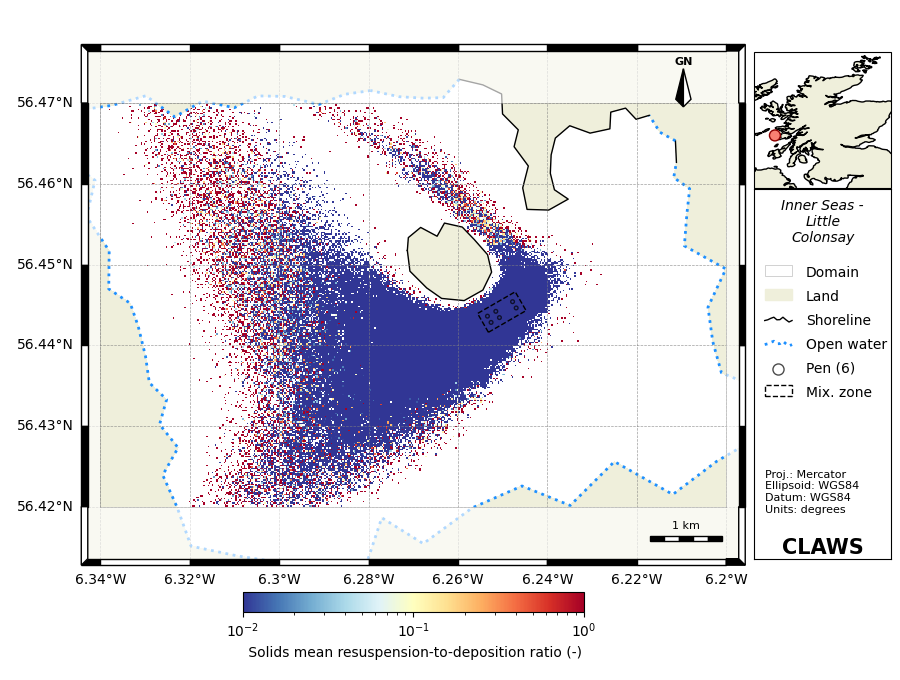
4. Waste - The waste model calculates the flux of particulate organic matter emanating from the salmon farm and its impact on the benthic community. Predictions of the fate of waste material (feed and faeces) for key parameters such as the footprint of the deposition on the sea floor and waste density levels.
5. E. coli - Dispersion and fate of Escherichia coli (E. coli) from raw sewage combined sewer overflows, agricultural run-off and other sources in rivers and estuaries.
6. Oyster larvae - Model for the transport and deposition of oyster larvae with multiple biological stages and active swimming behaviour.
7. Plastic litter - Model for the dispersion of plastic litter in rivers and estuaries including the development of a beaching model.
CLAWS aims at developing the necessary computational tools to allow practitioners to model the dispersion of bath treatment chemicals, feed and faeces waste, and nutrients from aquaculture sites such as salmon farms. If you would like to contribute or need support in the form of consulting services, please get in touch.